The Role of Pneumatic Welded Hydraulic Cylinder in Machinery
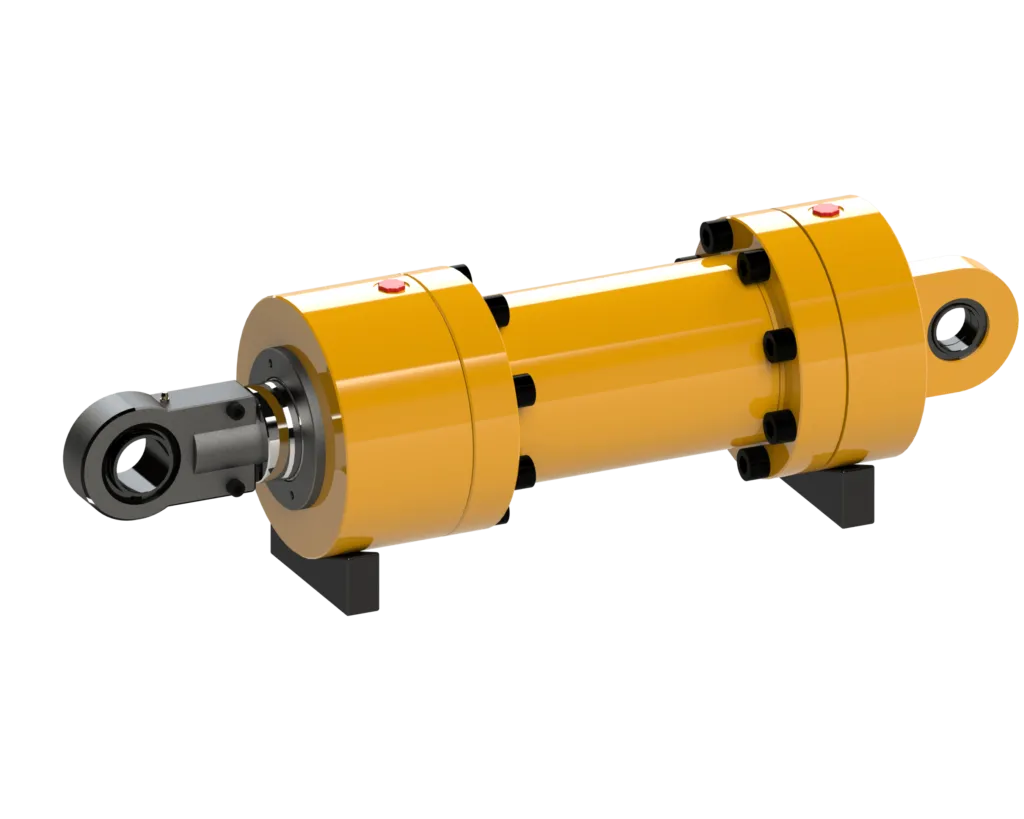
Design and Construction Characteristics
Composite Structure: The pneumatic welded hydraulic cylinder utilizes composite materials to enhance strength and durability in various working environments.
Lightweight Design: By optimizing design and using lightweight materials, the cylinder is made lighter to improve equipment flexibility and efficiency.
Sealing System: High-performance seals are employed to ensure excellent sealing performance under pneumatic and hydraulic pressure, preventing air and oil leakage.
Modular Design: The cylinder is designed modularly for easy maintenance and part replacement, enhancing equipment maintainability.
Construction Details
Welded Process: The cylinder undergoes a specific welding process, such as TIG or MIG, to ensure joint strength and sealing.
Precision Machining: High-precision equipment like CNC machines are used to ensure each part meets design requirements.
Pre-Welded Treatment: Material surfaces are cleaned and pretreated to remove impurities, improving welding quality.

Temperature Control Management: Temperature during welding is controlled to prevent material degradation or deformation.
Working Principle
The pneumatic welded hydraulic cylinder combines pneumatic and hydraulic technologies to achieve mechanical action through gas and liquid pressure.
Working Principle Description
The cylinder uses a combination of gas and liquid pressure to move a piston, providing mechanical force for various applications.
Types and Configurations
There are three main types of pneumatic welded hydraulic cylinders, each with unique configurations for specific industrial needs.
Type 1
Description of the first type of cylinder.
Type 2
Description of the second type of cylinder.
Type 3
Description of the third type of cylinder.
Advantages
High Efficiency – Fast Response: Pneumatic systems provide quick start and stop capabilities for rapid mechanical action.
Powerful Force: The cylinder can generate significant output force to handle heavy loads.
Precise Control – High Positioning Accuracy: Combining pneumatic and hydraulic technologies allows for precise piston positioning.
Adjustable: Operators can flexibly adjust working speed and force by regulating air pressure and hydraulic flow.
Wide Applicability – Versatility: Suitable for various industrial applications to meet diverse process requirements.
Advantages Description
Detailed descriptions of each advantage.
Application Scenarios
Various application scenarios of pneumatic welded hydraulic cylinders in different industries.
Welded Equipment
Application in welded robots, automatic welding machines, ensuring stable force and precise control.
Riveting and Assembly
Used in automotive manufacturing and shipbuilding for quick and accurate riveting and assembly tasks.
Automated Production Lines
Integrated into handling, sorting, and packaging machinery to enhance automation and efficiency.
Heavy Machinery
Employs as a power source in heavy machinery like excavators and forklifts for strong power support in harsh environments.
Design Considerations and Selection Criteria
Key factors to consider when designing and selecting pneumatic welded hydraulic cylinders.
Bearing Capacity
Exploring the load-bearing capacity of cylinders for various applications.
Sealing
Ensuring proper sealing to prevent leaks and maintain operational efficiency.
Durability, Safety, and Maintainability
Discussing the importance of cylinder durability, safety features, and easy maintenance.
Sealing and Lubrication
Details on seals and lubrication methods for pneumatic welded hydraulic cylinders.
Sealing
Use of piston seals, rod seals, and wear-resistant materials for improved performance.

Lubrication
Regularly filling the cylinder with hydraulic oil for lubrication to enhance longevity.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Suggested inspection and maintenance measures for optimal cylinder performance.
Regular Inspection
Importance of routine checks and maintenance to prevent issues.
Proper Lubrication
Ensuring correct lubrication to reduce wear and prolong cylinder life.
Seal Replacement and Calibration
Guidelines for seal replacement and calibration inspections to maintain efficiency.
Installation Guide
Step-by-step instructions for correctly installing pneumatic welded hydraulic cylinders.
Fault Diagnosis and Common Problems
Identification of potential faults and solutions for common issues in cylinder operation.
Key Questions
Answering important questions related to pneumatic welded hydraulic cylinders.
Question 1
Answer to the first question.
Question 2
Answer to the second question.

Question 3
Answer to the third question.
Long Tail Keywords
Explanation of three long tail keywords related to pneumatic welded hydraulic cylinders.
Company Focus
Introduction to our hydraulic cylinder replacement manufacturing company and services.
Content about the company’s product line, market presence, certifications, custom services, production facilities, and after-sales support.
Author: lyl