The Role of Pneumatic Welded Hydraulic Cylinder in Machinery
Design and Construction Characteristics
Composite Structure: The pneumatic welded hydraulic cylinder utilizes composite materials to enhance strength and durability for various working environments.
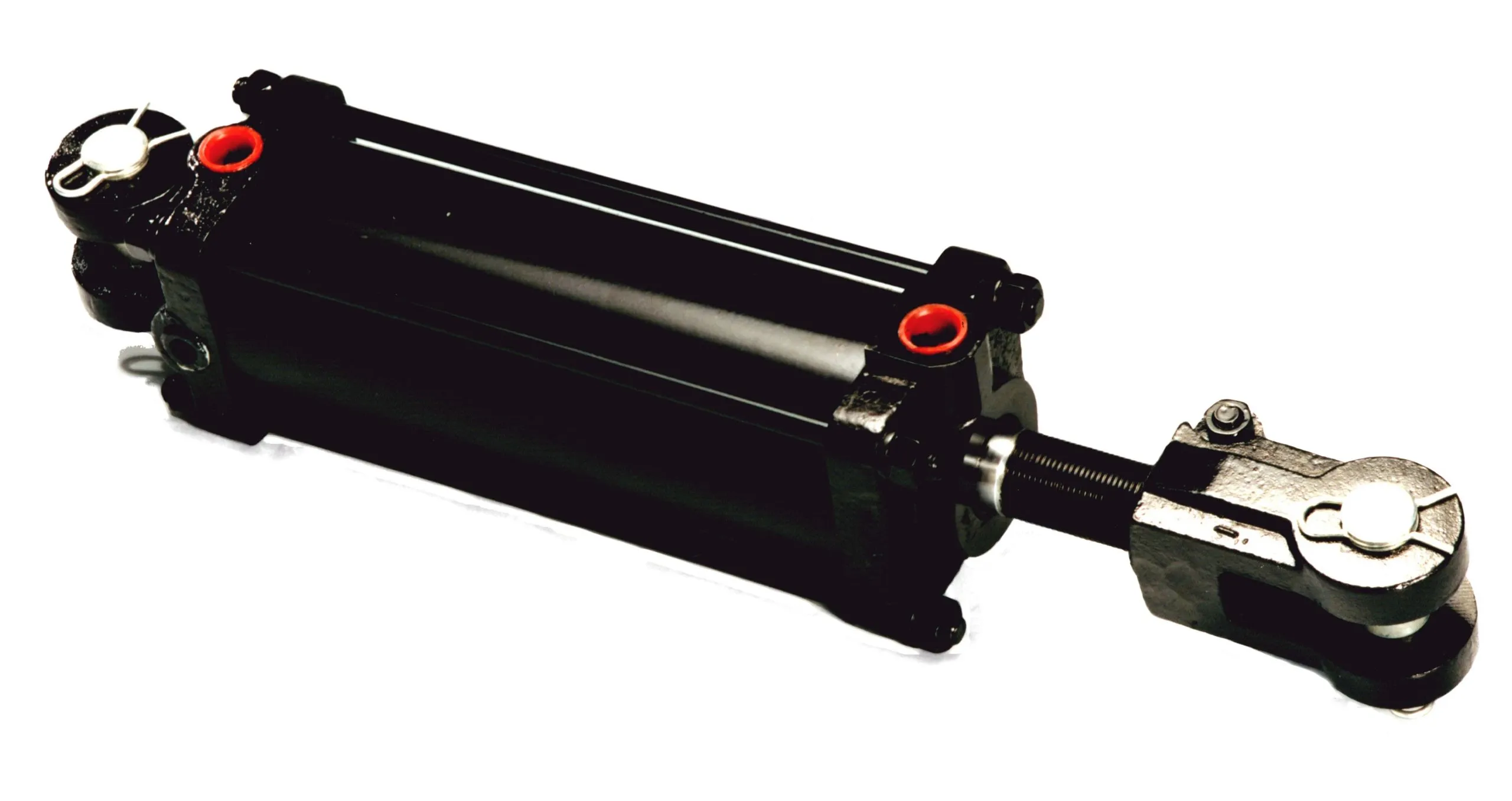

Lightweight Design: By using lightweight materials, the cylinder’s weight is reduced, enhancing overall equipment efficiency.
Sealing System: High-performance seals prevent air and oil leakage, ensuring optimal performance under pneumatic and hydraulic pressures.
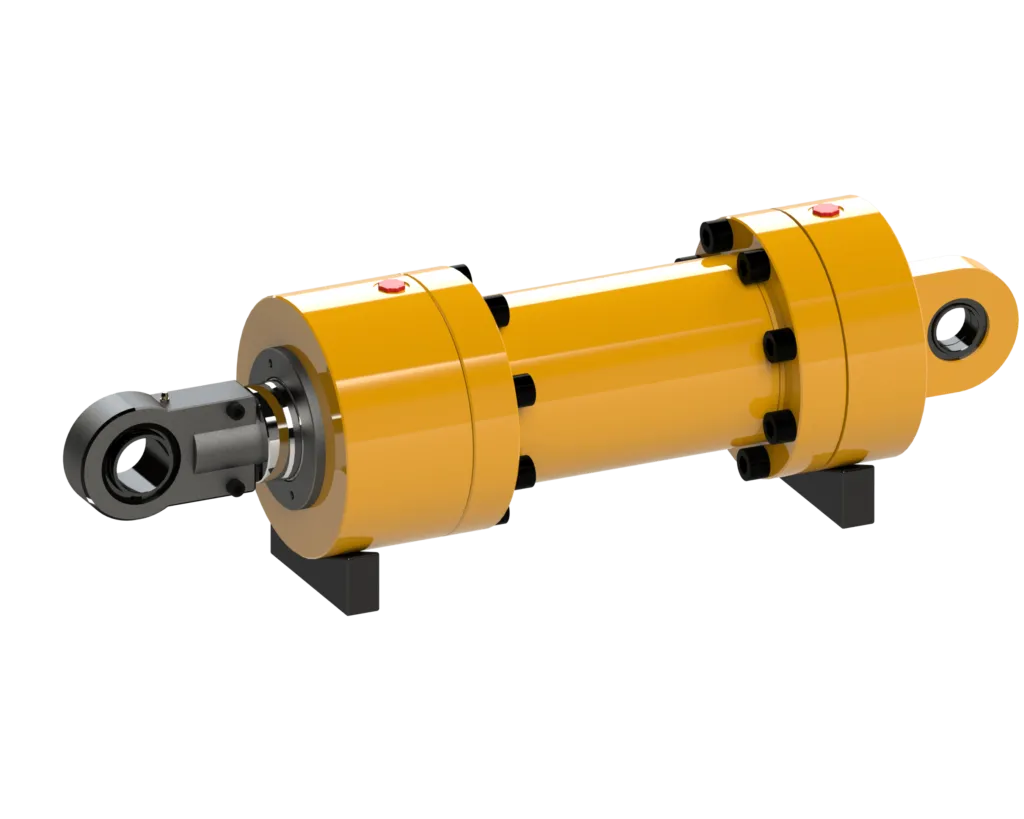
Modular Design: The cylinder features a modular design for easy maintenance and part replacement, improving equipment maintainability.
Construction Details
Welded Process: The cylinder undergoes TIG or MIG welding to ensure strong and sealed joints.
Precision Machining: High-precision CNC equipment is used to guarantee accurate part sizes and shapes.
Pre-Welded Treatment: Surface cleaning and pretreatment before welding improve the quality of welds.
Temperature Control Management: Precise temperature control during welding prevents material degradation.
Working Principle
The pneumatic welded hydraulic cylinder combines pneumatic and hydraulic technologies to achieve mechanical action through gas and liquid pressure.
Types and Configurations
1. Single-acting cylinder
2. Double-acting cylinder
3. Telescopic cylinder
Advantages
High Efficiency: Enables rapid response and high-frequency operation.
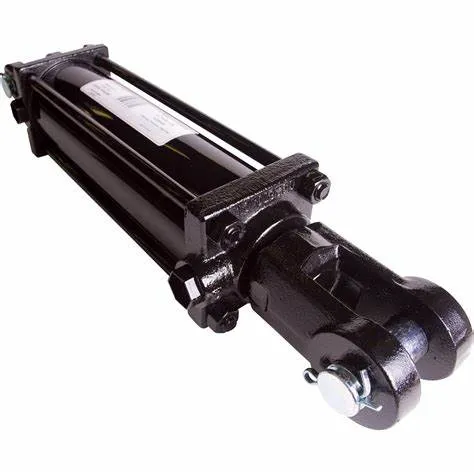

Powerful Force: Provides significant force output for heavy loads.
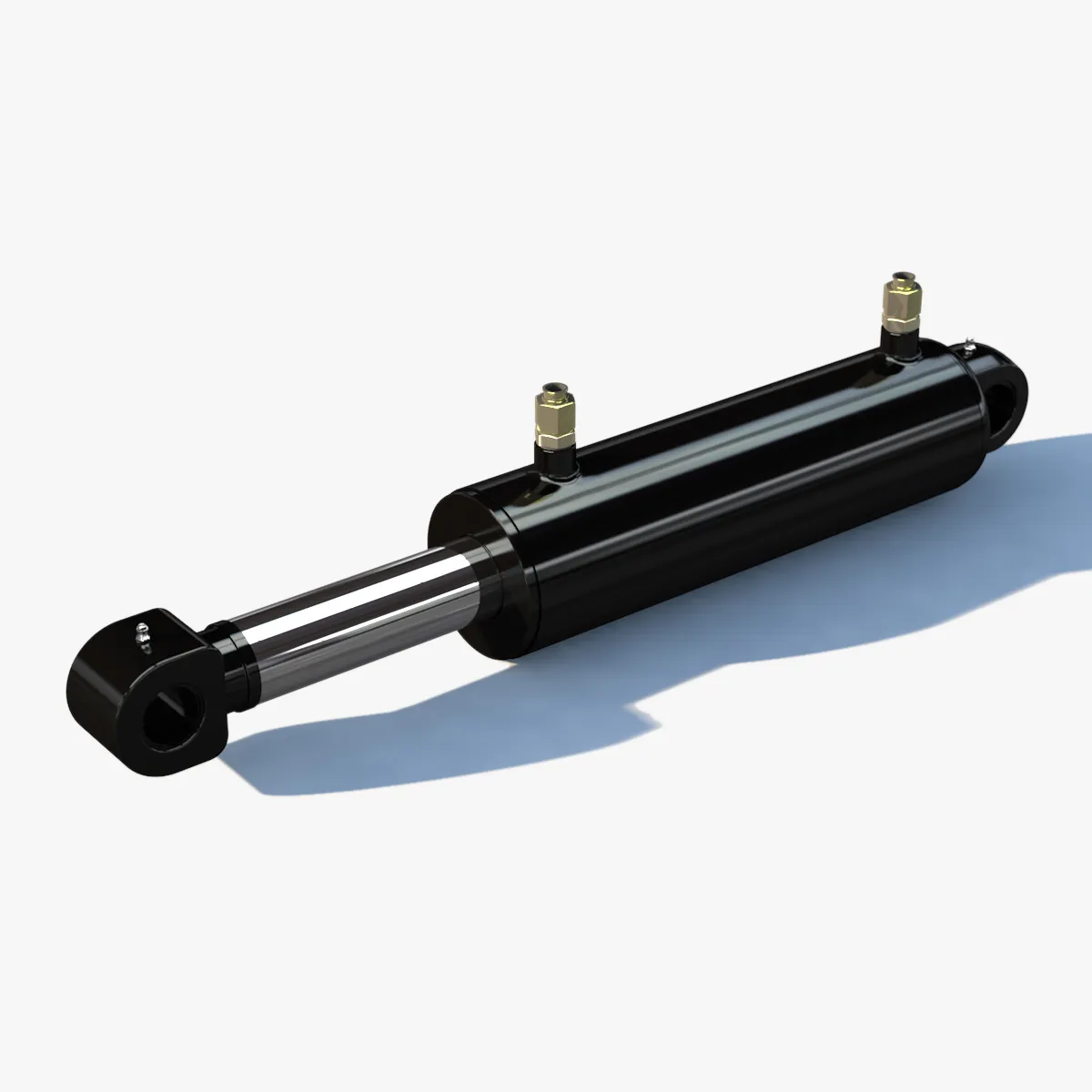

Precise Control: Achieves high positioning accuracy for precision processes.
Adjustable: Allows flexible adjustment of working speed and force.
Wide Applicability: Versatile for various industrial applications.
Application Scenarios
Welded Equipment: Stable force provision for robots and automatic welding machines.
Riveting and Assembly: Quick and accurate riveting in automotive and shipbuilding industries.
Automated Production Lines: Enhances work efficiency in handling and packaging machinery.
Heavy Machinery: Provides strong power support for excavators and forklifts.
Design Considerations and Selection Criteria
Bearing Capacity: Determines the maximum load the cylinder can handle.
Sealing: Ensures no leakage of air or oil.
Durability: Long-lasting performance under various conditions.
Safety: Focuses on user safety during operation.
Maintainability: Easy maintenance and part replacement.
Sealing and Lubrication
The cylinder utilizes various seals and fine surface treatments for wear resistance, requiring regular hydraulic oil lubrication.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance
1. Conduct regular inspections for wear and tear.
2. Ensure proper lubrication to prevent friction.
3. Replace seals and components as needed.
Installation Guide
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for correct installation procedures to ensure optimal performance.
Maintenance Tasks
1. Perform regular inspections.
2. Properly lubricate moving parts.
3. Replace worn seals and components.
Safety Considerations
Adhere to safety measures to prevent accidents during cylinder operation.
Fault Diagnosis and Common Problems
1. Cylinder not extending or retracting fully.
2. Oil leakage from the cylinder.
3. Inconsistent cylinder movement.
Three Questions About Pneumatic Welded Hydraulic Cylinder
1. How does a pneumatic hydraulic cylinder function?
2. What are the primary applications of pneumatic welded hydraulic cylinders?
3. What materials are commonly used in the construction of these cylinders?
Long Tail Keywords
1. High-pressure pneumatic hydraulic cylinder
2. Precision welded hydraulic cylinder
3. Composite material hydraulic cylinder
Company Overview
We are a leading hydraulic cylinder manufacturer offering a complete product line for domestic and international markets. Our company specializes in providing top-notch hydraulic cylinders and customized services to meet diverse industry needs.