Understanding Single-Acting Telescopic Hydraulic Cylinders
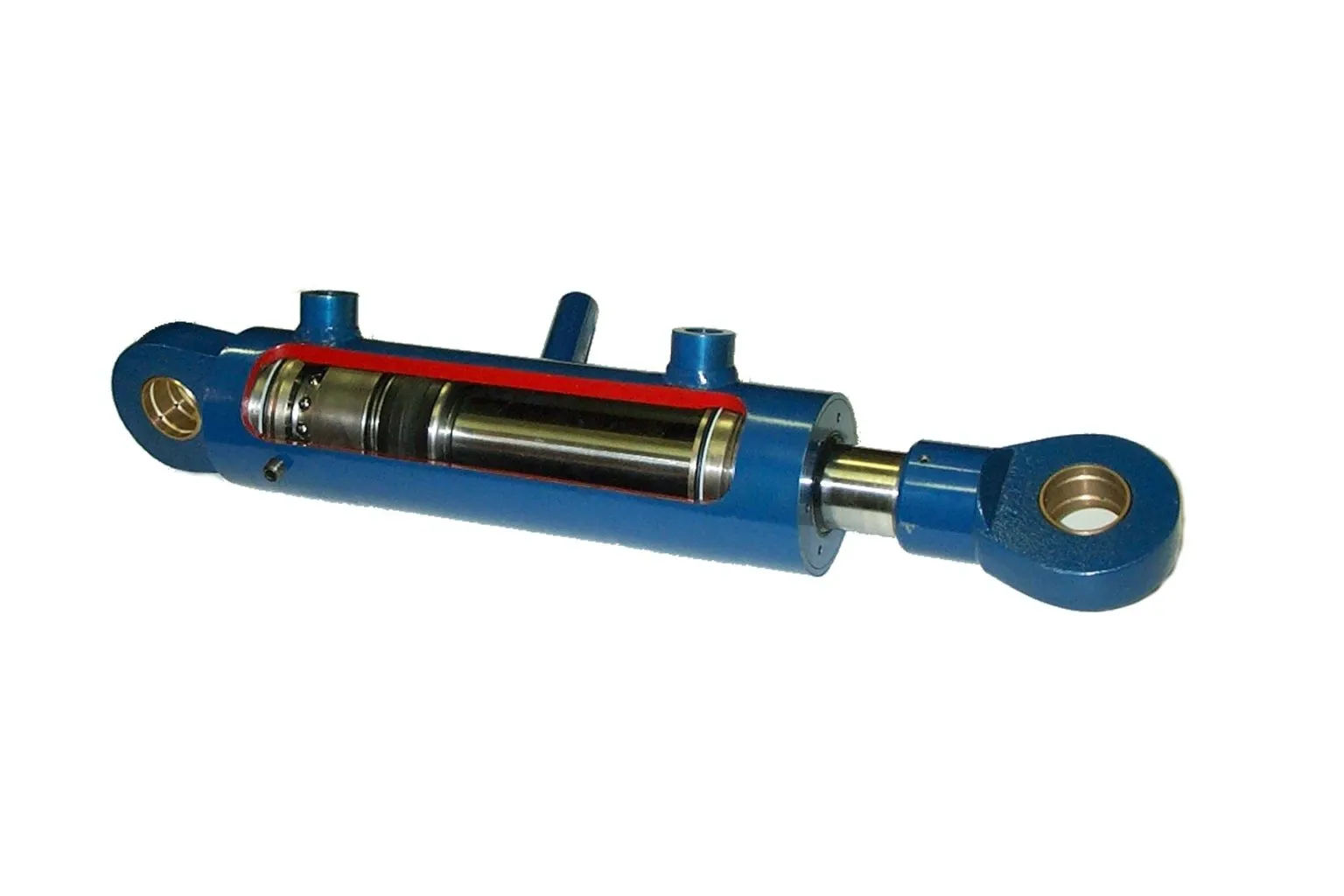

Introduction
In the world of hydraulic systems, the single-acting telescopic hydraulic cylinder plays a crucial role in various applications, especially in rail and transit scenarios. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of this specialized hydraulic component.
Definition and Composition
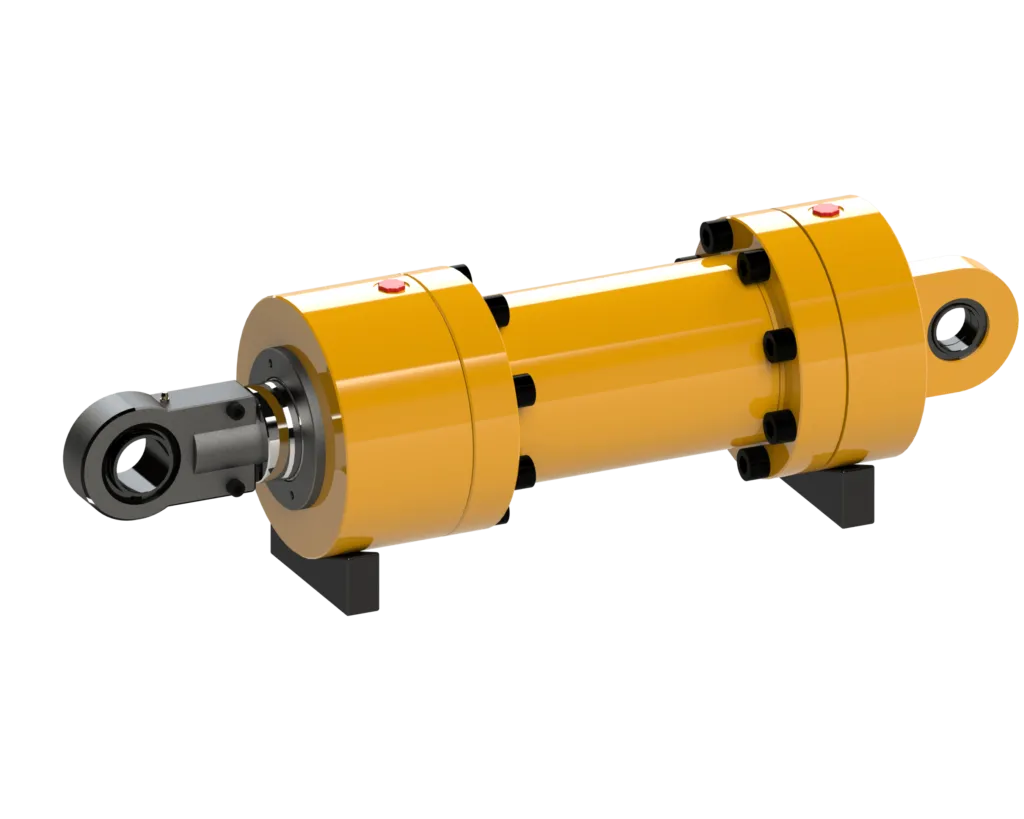
A single-acting telescopic hydraulic cylinder is a type of hydraulic cylinder that operates in one direction only. It consists of multiple stages that collapse into each other, allowing for a compact design with extended reach capabilities.
Design Principle
- The design principle of a single-acting telescopic hydraulic cylinder revolves around the use of hydraulic fluid to create linear motion.
- It typically includes a cylinder, piston rod, seals, and hydraulic oil to facilitate movement.
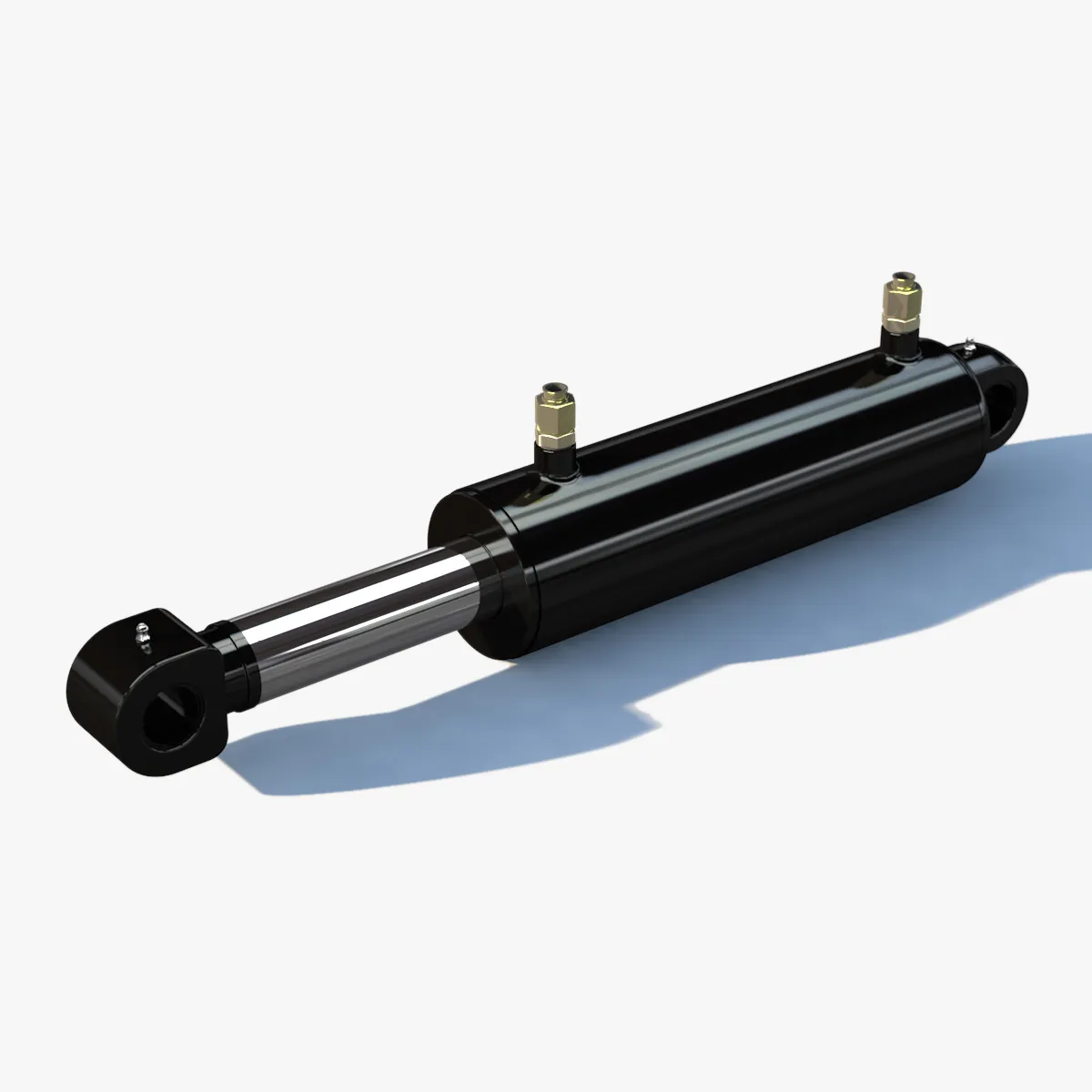

Telescopic Joint Description
The telescopic joint of this cylinder comprises internal and external stages that work together to extend and retract the cylinder efficiently.
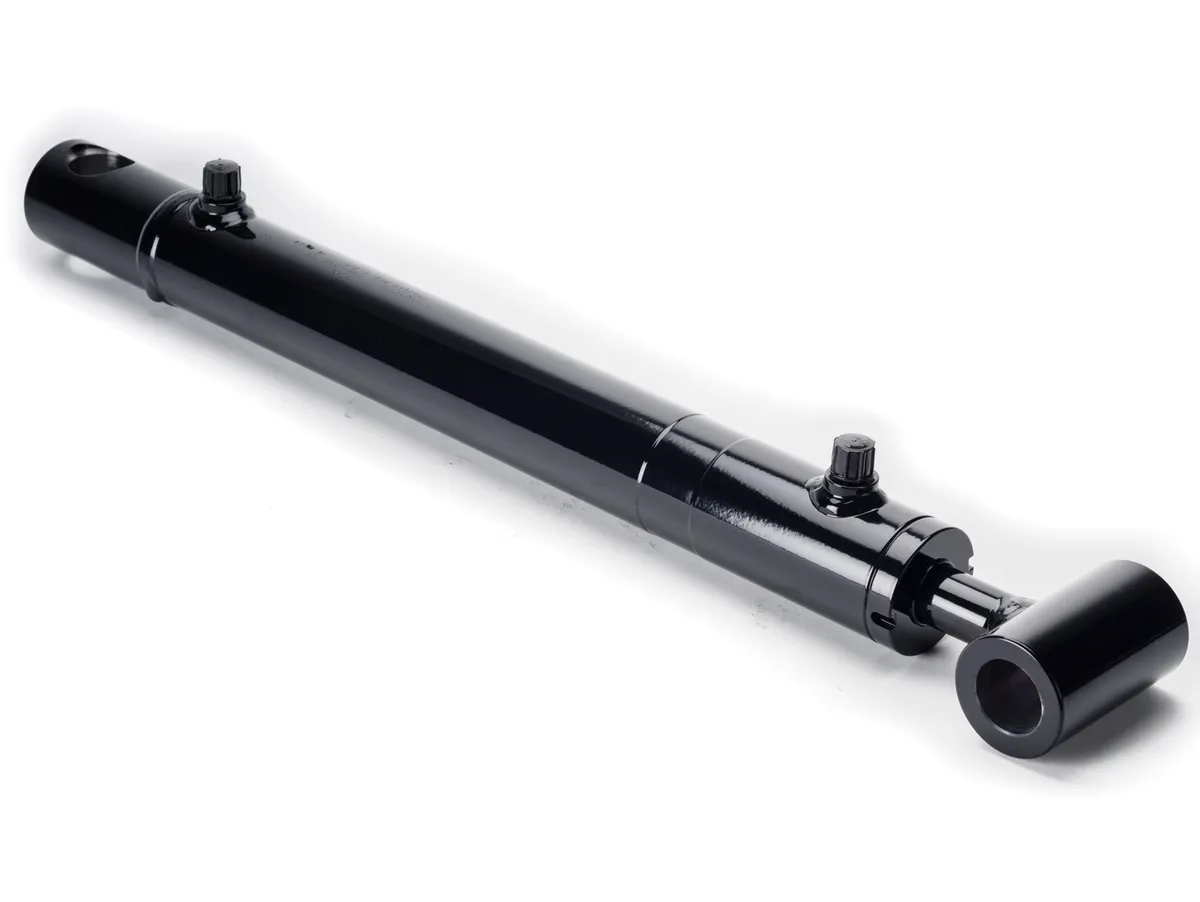

Working Principle
During operation, hydraulic fluid flows bidirectionally to enable the tension and contraction of the cylinder, providing independent extension and contraction movements.
Types and Configurations
There are three main types of single-acting hydraulic cylinders available, each with unique configurations tailored to specific applications.
Internal Components and Multistage Structure
The internal components of a single-acting telescopic hydraulic cylinder include a piston, chamber, special sealing mechanisms, guiding systems, and retracting mechanisms.
Advantages
The advantages of using a single-acting telescopic cylinder include precise positioning, force generation, stability, rigidity, and responsiveness.
Common Applications
Single-acting telescopic cylinders are widely used in material handling, construction equipment, agricultural machinery, special equipment, and more, due to their versatility and reliability.
Selection Considerations
When selecting a single-acting telescopic hydraulic cylinder, factors such as size range, inner diameter, stroke length, material durability, integrated functions, and installation options should be carefully considered.
Maintenance Tasks
Regular inspection of seals, bushings, hydraulic oil maintenance, and contamination control are essential maintenance tasks to ensure the longevity and performance of the cylinder.
Installation Steps
Proper installation steps for a single-acting telescopic hydraulic cylinder are crucial for optimal performance and safety.
Fault Diagnosis and Solutions
Common problems such as leakage, insufficient force, or unstable motion require troubleshooting tips and preventive measures to maintain operational efficiency.
Safety Standards and Regulations
Adhering to safety standards and regulations, including overload protection and emergency shutdown mechanisms, is critical for the safe operation of single-acting telescopic hydraulic cylinders.